How to study for the CFA exams (or any other finance exams for that matter)? Have you ever wondered if your current study methods are effective for passing your exams?
A comprehensive study called “Improving Students’ Learning With Effective Learning Techniques” by Dunlosky et al. (2013), may just help answer that.
More importantly, I’ve read through and applied the learnings of this study for the specific case of CFA, FRM and CAIA exams, with some of interesting findings that form the best practices for preparation of these challenging qualifications.
All nicely summarized for you in this guide on how to study effectively for exams. Read this before you start studying to have the best start!
Summary of this research paper on the most effective study techniques (Dunlosky et al. 2013)
Research approach
The goal of Dunlosky’s research paper was to provide reviews and general ratings that would be useful for readers to obtain a quick overview of what study method may work best for them.
This research paper applied an evidence-based approach in reviewing the efficacy of the 10 study methods across these 4 categories of variables:
- Learning Conditions,
- Student Characteristics,
- Materials, and
- Criterion Tasks.
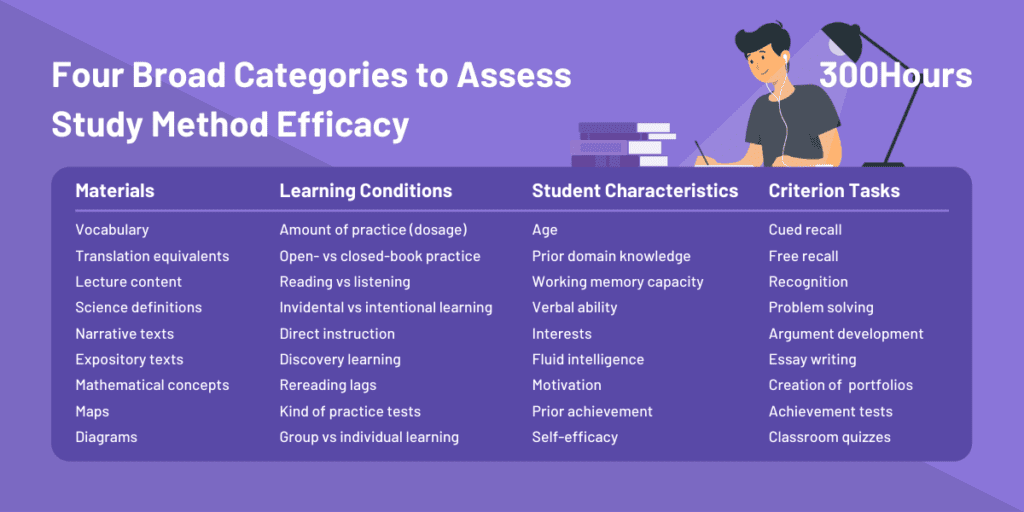
The 10 study techniques reviewed are fairly common and relatively easy to implement for any (motivated) student.
Here are their definitions and the research paper’s rating (i.e. “General Utility”) of their overall effectiveness in improving student achievement:
| Study Techniques | Definition | General Utility |
|---|---|---|
| Highlighting / Underlining | Marking potentially important texts when reading | Low |
| Keyword Mnemonic | Use keywords or mental imagery to associate verbal materials | Low |
| Imagery for Text | Form mental images of text materials when reading or listening | Low |
| Summarization | Writing summaries (of various lengths) of to-be-learned texts | Low |
| Rereading | Restudying text again after initial reading to increase retention | Low |
| Elaborative Interrogation | Generating an explanation for why an explicitly stated fact or concept is true | Moderate |
| Interleaved Practice | Implementing a schedule of practice that mixes different kinds of problems, or a schedule of study that mixes different kinds of materials, within a single study session | Moderate |
| Self-Explanation | Explaining how new information is related to known information, or explaining steps taken during problem solving | Moderate |
| Practice Testing | Self testing through practice tests | High |
| Distributed Practice | Implementing a schedule of practice that spreads out study activities over time | High |
So, what does this tell us?
Summarization, highlighting, keyword mnemonic, imagery use for text learning, and rereading are generally ineffective for learning
This is because:
- While summarization and imagery use for text learning are helpful in some criterion tasks, yet the conditions under which these techniques produce benefits are limited. More research is needed.
- The keyword mnemonic is difficult to implement in some contexts, and it seems to benefit students for a limited number of materials and for short retention intervals.
- Most students report rereading and highlighting, yet these techniques do not consistently boost students’ performance.
Elaborative interrogation, self-explanation, and interleaved practice are moderately effective for learning
The benefits of these techniques do generalize across some variables, but fell short of a high utility assessment because of limited evidence of their efficacy.
Nevertheless, these techniques are promising and useful in certain situations (detailed further below), with further research needed.
Practice testing and distributed practice are the most effective study techniques
These 2 study methods received a high utility rating because they benefit learners of different ages and abilities and have been shown to boost students’ performance across many criterion tasks and even in educational contexts.
Which study techniques are especially useful for CFA, FRM and CAIA exams?

A quick reminder: the “General Utility” assessment given by this research paper is an overall rating across 4 variables mentioned previously (Learning Conditions, Student Characteristics, Materials and Criterion Tasks).
For the purposes of CFA, FRM and CAIA exams, the Materials and Criterion Tasks categories are key. We need to see if these 10 learning strategies work particularly well in these 2 categories that are relevant for CFA exams, which mainly involve math problems, problem solving, essay writing, comprehension skills etc.
So, what I’ve done below is applied my interpretation of this research paper and generated a “CFA Exam Utility” column to assess the effectiveness of these 10 study methods with an extra emphasis on Materials and Criterion Tasks categories.
The “General Utility” column reflects the research paper’s original utility assessment across all categories. As you can see, there are some differences and a few interesting conclusions to make:

Least effective study techniques: Highlighting, mnemonics and imagery

Interestingly, common methods such as Highlighting/Underlining, Mnemonics and Imagery are the least effective for CFA exam preparations:
- This is because mental imagery techniques (Mnemonics and Imagery for Text) are only useful in a few instances with limited applicability overall for learning CFA exam materials – for example, you can’t use mnemonics to understand the discounted cashflow formula. You can probably use these techniques in a limited way to learn certain concepts in the CFA exams.
- In most situations, there is a lack of evidence that highlighting boosts study performance In fact, one study pointed out that highlighting is actually detrimental to making inferences, which is crucial for CFA exams.
Moderately useful study techniques: Elaborative interrogation, interleaved Practice, and (to some extent) rereading & summarization

In our view, these 4 study techniques are somewhat useful for certain aspects of CFA exams:
Rereading and Summarization
While Dunlosky et al.’s research paper gave these 2 strategies a low utility assessment, we felt that these are still useful if used selectively for the CFA exams.
These 2 methods are obviously more effective for remembering and learning materials, and performs less well for problem solving tasks – that’s where you need practice testing to reinforce your reading.
We find that rereading or summarizing small sections of the curriculum, especially after doing a practice test, can be helpful to reinforce your understanding of why you’ve got certain questions incorrect. In our view, CFA candidates shouldn’t reread the whole curriculum more than twice, or feel the need to summarize large sections of the curriculum – your time is better spent elsewhere such as doing practice tests (see next section).
Elaborative Interrogation
What this means in essence is the process of asking and explaining why certain stated facts are true (or not). This method is especially effective for factual materials (like Ethics, GIPS) where you just have to learn the concepts before explaining why a person has (or hasn’t) violated the Ethical Standards.
Although promising, this technique received a moderate utility rating because it has less evidence (so far) on whether elaborative interrogation facilitates recall or comprehension.
Interleaved Practice

The best way to understand this is that it is the opposite of “Blocked Practice”, i.e. all problems of one type are practiced, before moving on the next topic. In contrast, Interleaved Practice involves students practicing on a mix of different types of problems in one go.
This is interesting from a CFA exam angle, as candidates commonly do both Blocked Practice (e.g. doing end of chapter questions after reading a sub topic) and Interleaved Practice (doing timed mock practice exams which has a mix of topics).
Evidence on Interleaved vs. Block Practice shows a typical interleaving effect (Taylor & Rohrer 2010): during practice sessions, students who block-practised performed better than those who interleaved, but the performance is reversed when applied under actual tests (e.g. like the CFA exams). That sounds intuitive: doing similar problems right after learning/reading about it (Blocked Practice) is easy, but if you keep practicing and learning how to apply and discriminate between how to answer different questions in a mixed-question test (Interleaved Practice) that simulates real CFA exams, you’d perform better in actual tests.
In essence, Block Practice promotes quick learning and quick forgetting, whereas Interleaved Practice slows learning but leads to greater retention. This does explain why most CFA candidates get a really low score in their first few practice exams – it is because of the transition from Block Practice to Interleaved Practice!
Highly effective study techniques: Self explanation, practice testing & distributed practice

More importantly, this research paper affirms what we’ve been strong advocates of all along: practice makes perfect. A little moment of triumph to know that our experiences so far is backed by good solid empirical evidence!
Fact: testing improves learning and retention.
Practice testing and distributed practice proved to be most effective learning methods, but we would also like to add in self-explanation to this list given its usefulness in problem solving and comprehension.
Here are some examples of how to apply these in the context of CFA exam preparations:
Self-Explanation
This entails explaining your thought process on why you select an answer, or what logical steps you’ve taken to arrive at your answer.
We’ve added this in the highly effectively list for CFA exams (vs. the moderate rating in the original research paper), because this method is particularly useful during the constructed-response part of CFA Level 3, whereby jotting down your thought process and calculations in arriving to your conclusion is just as important as the accuracy of your answer itself.
Practice Testing
This means any self administered testing that you can do on your own in the process of studying for the CFA exams, e.g. using flashcards to help recall new concepts, question banks, or doing mock practice papers.
There’s loads of evidence that practice testing improves learning across an impressive range of practice-test formats, types of material, learner ages, outcome measures, and retention intervals.
FYI – we also have a bunch of free practice tests available for our readers at every CFA level!
Distributed Practice – the opposite of cramming
Given the same amount of study time for one level of the CFA exam (an average of 300 hours), it is more effective to spread your studies over time, rather than cramming it all in in the last month.
The empirical evidence for the benefits of distributed practice (vs. cramming) is very robust. Spacing out your learning into bite-sized chunks improves long term retention, just like what we’ve been recommending all along by starting your studies around 6 months before the CFA exams.
What Have We Learned on How To Study Effectively

Do these, they are crazy useful for your studies
- Use the free 300 Hours Study Planner, it helps you manage your studies at a good pace.
- Start your studies around 6 months before and space it out instead of cramming (but if emergency strikes here’s how to cram anyway, since cramming is better than not studying at all!). You can keep track of deadlines with our CFA Exam Calendar, which you can sync to your own personal one.
- Leave around 4-6 weeks before the exam free to complete 4-6 sets of practice exams, preferably under time constraint just like the real exam. Check where you’ve gone wrong and reason/ask why you chose that (wrong) answer. Rinse and repeat.
Do these sometimes
- You can make summary notes, tables, flash cards, mind maps etc (whatever works for you) to summarize certain complex concepts or topics. NOT for the whole CFA exam material though, it takes too much time.
- Reread subtopics that you’ve got wrong in your practice exams to plug the gap in your knowledge.
- Explain (whether to yourself out loud) or help others on the forum especially on factual materials (e.g. the definition of LIFO Reserve) that you need to know.
- Do both end of chapter (EOC) questions to reinforce learning of new materials, question banks and practice exams (that mixes up questions from different topics) for maximum impact.
Don’t do these

- Don’t try to learn how to have photographic memory when reading. It’s hard. And nearly impossible with CFA exam material.
- Mnemonics have some limited use. It does provide some variety in recalling materials.
- Last of all, highlighting or underlining texts. Probably harmless if you still want to do it. Just know that highlighting stuff may not necessarily make you learn stuff any better. It’s proven.
I’m guilty as charged for the occasional underlining of texts, urge to summarize everything and rereading (instead of practicing).
What about you? What study methods do you normally use and how did you find them? I’d love to hear your thoughts in the comments below!
Meanwhile, here are some other related articles that you may find useful:
- Free and Upgraded – 300Hours CFA Study Planner
- 18 Actionable Ways To Improve Memory For Studying [CFA Exam Edition]
- How Many CFA Practice Exams Should You Be Completing? Here’s What Our Research Says
- 2025 CFA Exam Curriculum and Topic Weight Changes
- CFA Level 1 Topics: What Is The Best Study Session Order?
- CFA Level 2 Topics: What Is The Best Study Session Order?
- CFA Level 3 Topics: What Is The Best Study Session Order?

I have a question about practice exams, quiz banks, etc being the most effective study method. Does that assume one has already read books and other study materials at least once so they actually have a solid-ish foundation when taking the quizzes? Or could one just take the quizzes and go back and read later if something truly doesn’t make sense?
For CFA exams, in my experience it is hard to do quizzes without reading the materials first for a base understanding. If you approach quizzes without reading much materials, while possibly doable, getting most of them incorrect and then having to refer to books anyway (which is a strategy) is great for when you’re running out of time. Personally I’d recommend going through the books and making sure you read them once and stop 4-6 weeks before exams to focus on practice questions fully to consolidate your learning.
That totally makes sense. I’m actually working on the CFP exam, and from what I can tell from other articles on 300Hours is equivalent to the CFA exam level 2 or 3 in difficulty, I can’t remember which exactly. I graduated from college with a bachelor’s degree that covered all of the topics in the CFP exam, so I have something of a base understanding, but it’s been almost 3 years since I graduated. I’ve semi-kept up with those topics over the years, but I’ve forgotten a lot of stuff. All of that to say, reading is definitely not my preferred study method, so I was wondering if I should just focus on practice quizzes.
Oooh this is a hard one Mike, there is no one ‘right’ study method as all of us absorb and learn things differently. I’d say for more ‘factual’ topics with less calculations/application, it is possible and perhaps sensible to dive straight into practice quizzes and learn from what you get wrong, but for topics which require deeper understanding, having a quick read through first may help before attempting quizzes. I’d say try and experiment with both and see how you fare, and adjust your strategy by topic accordingly.
Very insightful article. Will use the practice test and distributed test in my upcoming exam in May 2022. Will let you know the results and impact of these techniques. Thanks.
You’re welcome – let us know how it goes!
Great article, just like the rest of the content on this website, thank you guys for creating these insanely useful guides! And without invasive ads! Also love your emails.
Thanks so much TPL! We do prioritize our readers’ experience and benefit so it’s great to see that getting noticed!
Excellent Article!
Thank you!
Very good article and tips. I am completely guilty of summarizing and it is taking too much time, so I will take your advice to pick difficult concepts now and not everything.
Thank you!
You’re welcome @LSV. I did this mistake when I was an L2 candidate too, and it was madness trying to catch up when I fell behind the study schedule. Best of luck for the exams!